线程创建的三种方式
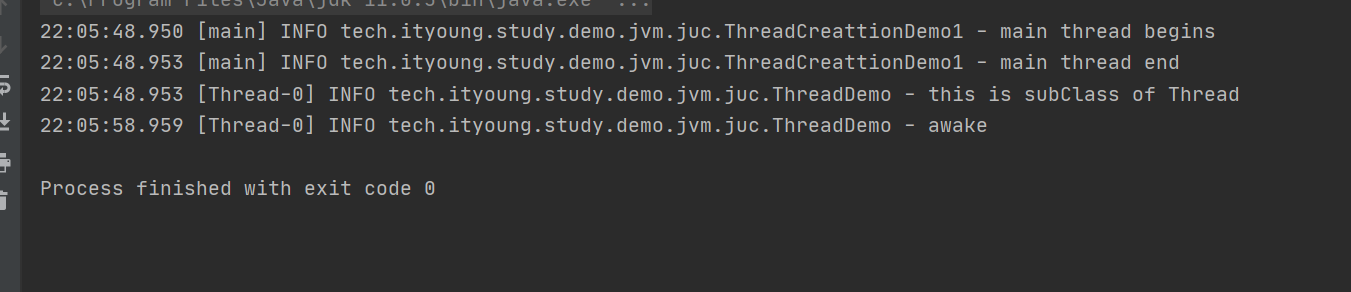
主线程不会等待子线程结束
Java进程会等待所有线程结束
三种方式本质都是在thread构造函数中传入runnable接口的实现对象
继承Thread类并复写thread中的run方法
package tech.ityoung.study.demo.jvm.juc;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
@Slf4j
public class ThreadCreattionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
log.info("main thread begins");
ThreadDemo demo = new ThreadDemo();
demo.start();
log.info("main thread end");
}
}
@Slf4j
class ThreadDemo extends Thread {
@SneakyThrows
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("this is subClass of Thread");
Thread.sleep(10000);
log.info("awake");
}
}
- 匿名内部类本质上还是继承Thread类
new Thread("sss"){
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("匿名内部类");
}
};
传入runnable接口
public static void main(String[] args) {
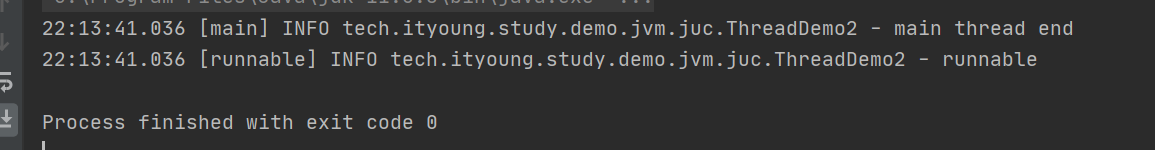
Thread runnable = new Thread(() -> {
log.info("runnable");
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "runnable");
runnable.start();
log.info("main thread end");
}
FutureTask
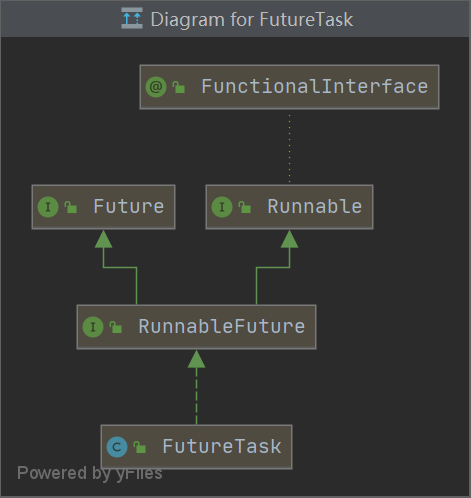
- FutureTask实现RunnableFuture,RunnableFuture继承Runnable和Future
- FutureTask自身有实现run方法,故构造方法传入callable
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
/**
* Sets this Future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}
@Slf4j
public class FutureTaskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
// 创建任务对象
FutureTask<Integer> task3 = new FutureTask<>(() -> {
log.debug("hello");
return 100;
});
// 参数1 是任务对象; 参数2 是线程名字,推荐
new Thread(task3, "t3").start();
// 主线程阻塞,同步等待 task 执行完毕的结果
Integer result = task3.get();
log.debug("结果是:{}", result);
}
}
线程打断interrupt
线程打断状态
获取状态
Thread.interrupted();
Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
- join、sleep、wait方法会以抛异常的方式提示打断,而不会改变打断标记
@Slf4j
public class InterruptDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.info("start sleep...");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
t1.interrupt();
log.info("interrupt status of ti:{}", t1.isInterrupted());
}
}
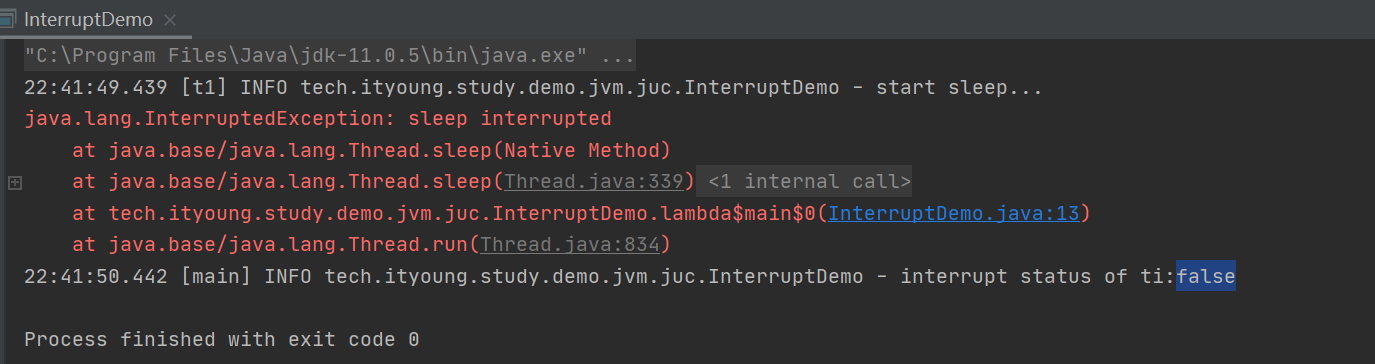
- 正常运行的程序被打断程序并不会自己停止运行
- 通过判断打断状态可以主动停止线程
@Slf4j
public class InterruptDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
boolean interrupted = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
if (interrupted) {
break;
}
}
}, "t1");
t1.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
log.info("interrupt begin");
t1.interrupt();
}
}
两阶段终止模式
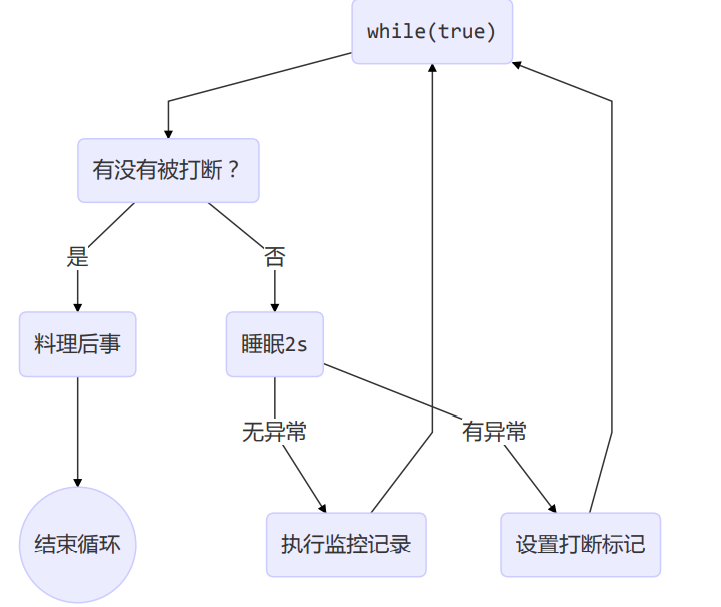
yield与sleep
sleep
- 调用 sleep 会让当前线程从 Running 进入 Timed Waiting 状态(阻塞)
- 其它线程可以使用 interrupt 方法打断正在睡眠的线程,这时 sleep 方法会抛出 InterruptedException
- 睡眠结束后的线程未必会立刻得到执行
- 建议用 TimeUnit 的 sleep 代替 Thread 的 sleep 来获得更好的可读性
yield
- 调用 yield 会让当前线程从 Running 进入 Runnable 就绪状态,然后调度执行其它线程
- 具体的实现依赖于操作系统的任务调度器
public class YieldDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
Thread.yield();
System.out.println("------------->t1:count = " + count++);
}
}, "t1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("--------------------------------------------->t2:count = " + count++);
}
}, "t2");
t2.start();
t1.start();
}
}
有时候yield并没有什么明显的实际效果
park
- park线程被打断不会改变isInterrupt状态
- wait、sleep等会清空isInterrupt状态
- interrupted()会改变interrupt状态
- interrupt后无法重新被park,需要清除状态Thread.interrupted(),返回打断状态并清除状态
 Stephen Young
Stephen Young

评论前必须登录!
注册